What is Biceps Tendonitis?
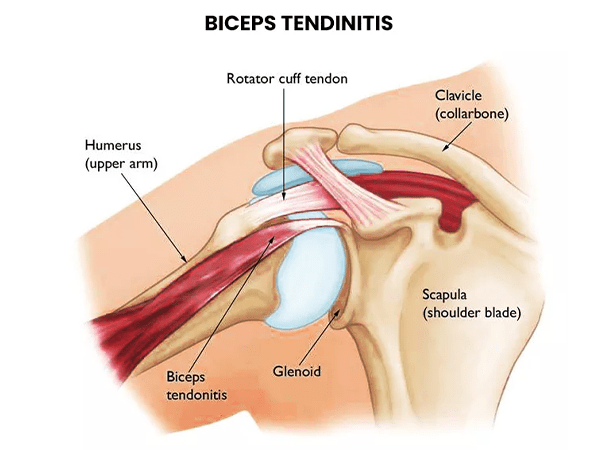
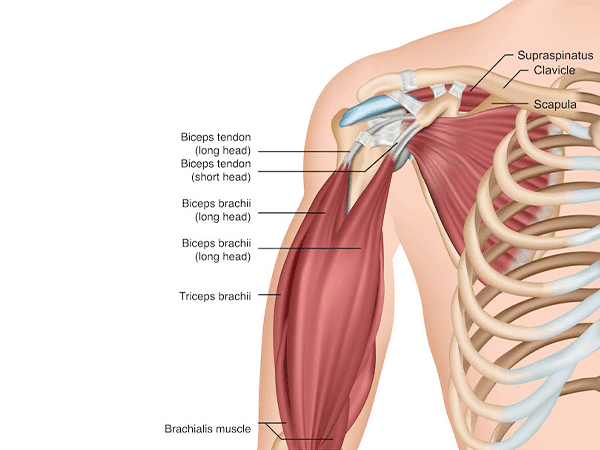
Biceps tendonitis is an inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon. The long head of the biceps tendon is a cord-like structure that connects the biceps muscle to the bone in the shoulder socket. It is a common condition that can be caused by overuse, repetitive motions, or injury.
The most common symptom of biceps tendonitis is pain in the front of the shoulder. The pain may be sharp or dull and may be worse when you move your arm. Other symptoms may include:
Weakness in the arm
Swelling and tenderness in the front of the shoulder
Difficulty rotating your arm
A popping or grinding sensation in the shoulder
Biceps tendonitis is usually diagnosed based on your medical history and physical examination. Your doctor may order imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to rule out other conditions.
Biceps tendonitis is usually treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Your doctor may also prescribe medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), to help relieve pain and inflammation. In some cases, physical therapy may be helpful.
Most cases of biceps tendonitis improve with rest and treatment. However, if the condition is severe or does not respond to treatment, surgery may be necessary to repair the tendon.
What are the Symptoms of Biceps Tendonitis?
The symptoms of biceps tendonitis include:
- Pain in the front of the shoulder
- Pain when lifting the arm overhead
- Pain when rotating the forearm
- Tenderness to touch in the front of the shoulder.
- Weakness in the biceps muscle
- A popping or snapping sensation in the shoulder.
Who Gets Biceps Tendonitis?
Biceps tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendons that connect the biceps muscle, at the front of your arm, to the shoulder and the elbow. It is most caused by overuse but can also be caused by a sudden injury to the tendon.
People who are most at risk for biceps tendinitis include:
- Athletes who participate in sports that require repetitive overhead motion, such as baseball, swimming, and tennis.
- People who do jobs that require repetitive overhead motion, such as painting, carpentry, and masonry
- People who have a history of shoulder injuries
- People who have weak or inflexible shoulder muscles
The symptoms of biceps tendinitis include:
- Pain in the front of the shoulder, especially when lifting or using the arm.
- Tenderness over the Biceps tendon
- Swelling and redness around the Biceps tendon
- Weakness in the biceps muscle
- Difficulty reaching overhead or behind the back.
What Causes Biceps Tendonitis?
Biceps tendonitis is an inflammation of the tendons that connect the biceps muscle to the shoulder and elbow. It is a common condition that can be caused by several factors, including:
Repetitive use: Activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as swinging a baseball bat, swimming, or playing tennis, can put stress on the biceps tendon and lead to inflammation.
Overuse: Lifting heavy objects or doing other activities that put a lot of stress on the biceps muscle can also lead to inflammation of the tendons.
Injury: A sudden injury, such as a fall or a direct blow to the arm, can also damage the biceps tendon and cause inflammation.
Age: As people age, the tendons in their bodies tend to become weaker and more susceptible to injury. This is why biceps tendonitis is more common in older adults.
Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, can weaken the tendons and make them more likely to become inflamed.
The symptoms of biceps tendonitis can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation. Some people may experience only mild pain and discomfort, while others may have severe pain that makes it difficult to use the arm. Other symptoms may include:
Swelling
Tenderness
Weakness
Crepitus (a grating or popping sensation when moving the arm)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment. Treatment for biceps tendonitis typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). In some cases, your doctor may also prescribe medication to reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the tendon.
With proper treatment, most people with biceps tendonitis make a full recovery. However, it is important to be patient and to allow the tendon time to heal. Returning to activities too soon can make the condition worse.
How is Biceps Tendonitis Diagnosed?
Biceps tendonitis is inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon, which is a thick cord of tissue that connects the biceps muscle to the elbow. It is a common condition that can be caused by overuse, repetitive motions, or trauma.
The diagnosis of biceps tendonitis is typically made by a doctor or other healthcare professional based on your medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests.
During your medical history, your doctor will ask you about your symptoms, including when they started, what makes them worse, and what makes them better. They will also ask you about your activities and hobbies, and whether you have any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to your symptoms.
During your physical examination, your doctor will examine your shoulder and elbow for tenderness, swelling, and weakness. They will also test your range of motion and strength.
