Knee arthritis can be caused by several factors, including:
Age: Knee arthritis is more common in people over the age of 50.
Previous injury: A previous injury to the knee, such as a torn ligament or cartilage, can increase the risk of developing knee arthritis.
Obesity: Excess weight can put extra stress on the knees, increasing the risk of arthritis.
Genetics: Some people are more likely to develop knee arthritis due to their genes.
The symptoms of knee arthritis can vary from person to person. Some people may experience only mild pain, while others may have severe pain that makes it difficult to walk or participate in activities. Other symptoms of knee arthritis include:
Stiffness: The knee may feel stiff, especially in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
Swelling: The knee may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch.
Crepitus:The knee may make a creaking or popping sound when it is moved.
Weakness: The muscles around the knee may become weak, making it difficult to support weight or walk.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of knee arthritis, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. There is no cure for knee arthritis, but there are treatments that can help to relieve pain, improve function, and slow the progression of the disease.
Treatment for knee arthritis may include
Medications: There are several medications that can help to relieve pain and inflammation associated with knee arthritis. These medications may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, or corticosteroids.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the knee.
Weight loss: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help to reduce the stress on your knees and improve symptoms.
Arthroscopic surgery: In some cases, arthroscopic surgery may be used to remove damaged cartilage or bone spurs, or to repair torn ligaments or cartilage.
Total knee replacement: In severe cases, total knee replacement may be necessary to relieve pain and improve function.
Knee arthritis can be a disabling condition, but there are treatments that can help to improve symptoms and quality of life. If you are experiencing pain or stiffness in your knees, it is important to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
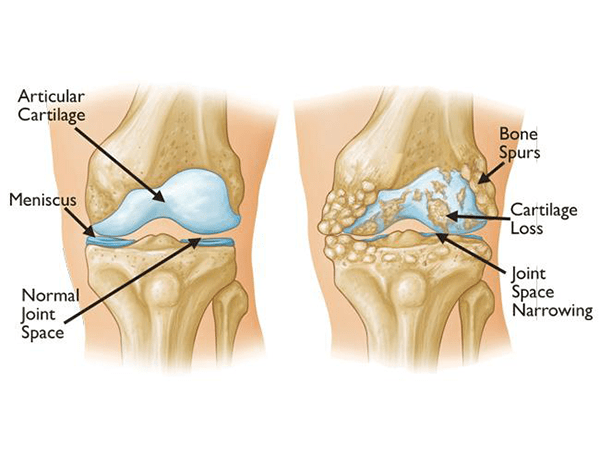
What is Osteoarthritis of the Knee?
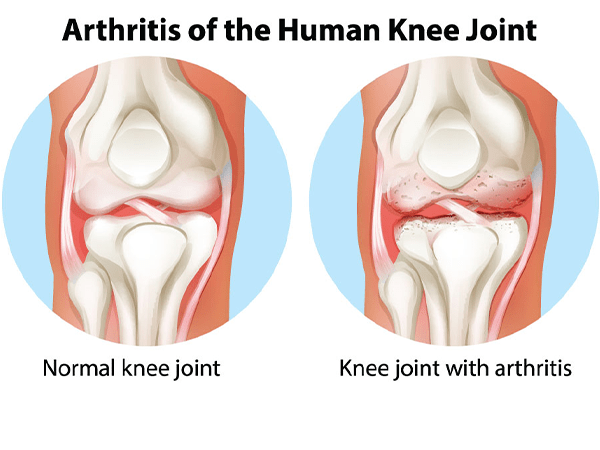
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a type of arthritis that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint breaks down. Cartilage is a smooth, slippery tissue that helps the bones in the knee joint move smoothly against each other. When the cartilage breaks down, the bones rub together, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is the most common type of arthritis in the knee. It is most common in people over the age of 50, but it can occur in younger people, too. It is more common in women than in men.
The exact cause of osteoarthritis of the knee is not known. However, it is thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including:
Weight
Injury to the knee
Occupations that require a lot of kneeling or squatting
Genetic factors
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee can vary from person to person. They may include:
Pain in the knee, especially when walking, climbing stairs, or kneeling.
Stiffness in the knee, especially in the morning or after sitting for a long time
Swelling in the knee
Crepitus (a crackling or popping sound when the knee moves)
Weakness in the knee
Loss of range of motion in the knee
If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment.
There is no cure for osteoarthritis of the knee, but there are treatments that can help to relieve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. These treatments may include:
Weight loss: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help to reduce stress on the knee joint.
Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help to relieve pain. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the knee.
Injections: Injections of cortisone or hyaluronic acid can help to relieve pain and inflammation.
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the knee joint.
If you have osteoarthritis of the knee, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that will help you to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
